 |
| Structure |
Normally, enzymes function as catalysts. Enzymes speed up a chemical reaction by loweing the activation energy needed to start the reaction.
Also, enzymes are required in minute amounts. Enzymes are very efficient molecules. They remain unchanged in the reactions they catalyse, the same enzyme molecules can be used over and over again. Enzymes are unique that each chemical reaction inside a cell is catalysed by a unique enzyme. (AKA enzyme specificity) Only molecules with exactly the right shapes will bind to the enzyme and react. These are the reactant , or substrate, molecules.And, the part of the enzyme to which the reactant binds is called the active site.
A substrate is ought to fit into an enzyme's active site. (Lock and Key Hypothesis: The enzyme is the lock, and the reactant is the key.)
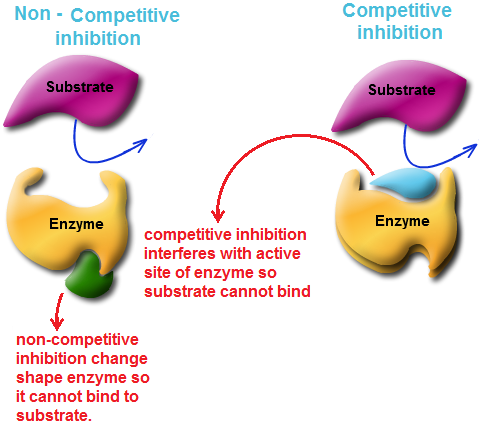
Moreover, there are two types of enzyme inhibitors: one is called competitive inhibitor, and the other one is called non-competitive inhibitor.
Last but not least, temperature and pH values would affect enzymes. Enzymes would change shapes under certain temperature/ pH level; therefore, shape changes would affect the function of enzymes.
 |
| Summary :) |









No comments:
Post a Comment